|
|
This task explains how to see if you need to set additional constraints to the components that make the assembly. |
|
|
The degrees of freedom analysis is performed
from assembly constraints only. This is mean that constraints from design
in context or assembly pattern are not taken into account. The analysis is performed from the active component and its child components set, but you must know that:
Translations can be performed in a plane is represented by two vectors. These vectors define the translation plane but depending on the geometry, they can constitute an orthonormal system or not. In other words, a planar translation which normal to the plane has the coordinates (x=0, y=1, z=0) can sometimes be represented by:
|
|
|
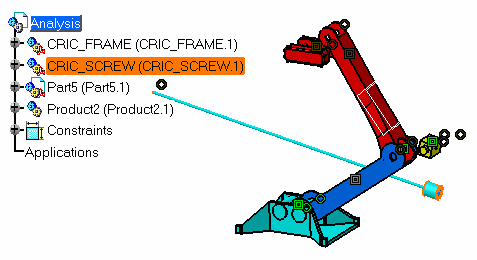
Open the Assembly_07.CATProduct CATProduct document. |
|
|
|
 |
|
 |
|
|
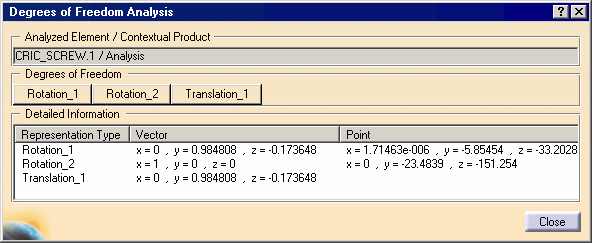
The dialog box displays all rotations and translations that remain possible for the selected component. In our scenario, you can rotate CRIC_SCREW (CRIC_SCREW.1) in two ways or translate it in one way. |
|
|
If you look at the geometry, you can notice that these rotations and translations are represented in yellow. |
|
|
|
|
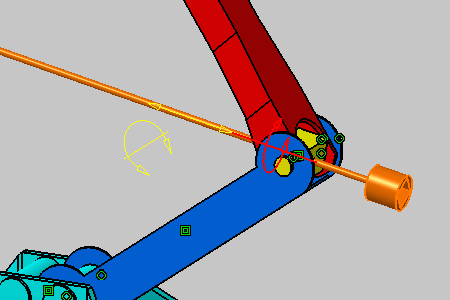
The graphic element representing this possible rotation is now highlighted in the geometry for easy identification. |
|
 |
|
|
As detailed in the dialog box, you can perform a rotation around the vector which coordinates are x=1, y=0 and z=0 and using the point with coordinates x=0, y=-23.4839 and z=-151.254 as the rotation center. |
|
|
|
|
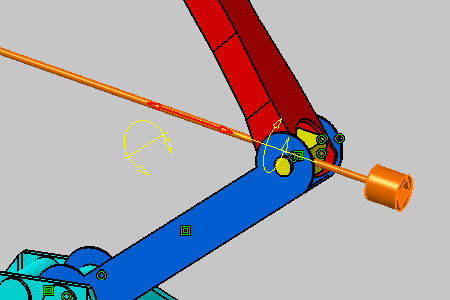
The graphic element representing this possible rotation is now highlighted too. |
|
 |
|
|
As detailed in the dialog box, you can perform a translation along the vector which coordinates are x=0, y=0.984808 and z=-0.173648. |
|
|
![]()