The input can be curves or edges of surfaces.
-
Make Geometrical Set.1 the Define in Work Object.
-
Click Discretize Curves
 .
.
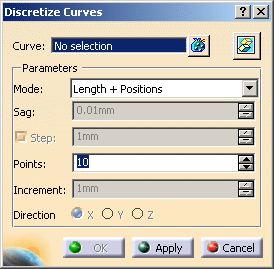
The Discretize Curves dialog box is displayed:
-
Select the curve to process (3D Curve.1).
Multi-selection is available.
is available.
 is available to hide or show the selection.
is available to hide or show the selection. -
Select a discretization mode from the Mode drop-down list:

-
Key-in the parameters requested by the mode you have selected.
-
Click Apply to visualize the result and OK to validate and exit the dialog box.
A Discretize Curves.1 feature is created in the Define in Work Object.

Modes and Parameters
In the examples below, the input curve looks like this:
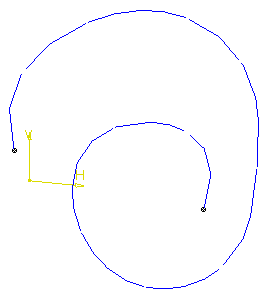
When selected, its color is orange. The scan is displayed in black.
Chord
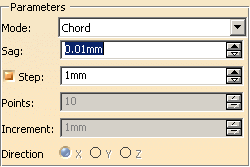
Sag:
Represents the maximum distance between the input curve and the theoretical
chord connecting two successive positions of the scan.
Step:
Optional. Represents the maximum distance between two successive positions
of the scan.
Examples:
Sag=0.1 mm, no step
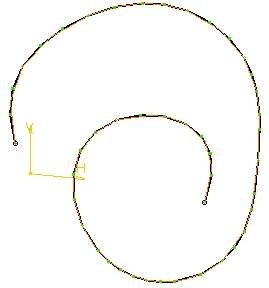
Sag=10 mm, no step
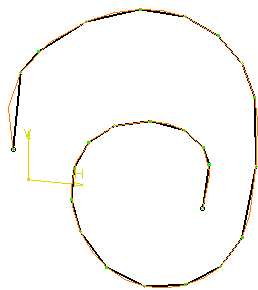
Sag=10 mm, Step=1 mm
Length + Positions

Points:
Is the number of positions N. The length of the curve is divided by (N-1,
providing a constant curve-length increment.
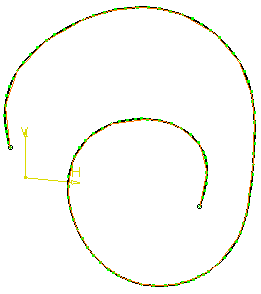
Example: Points=15
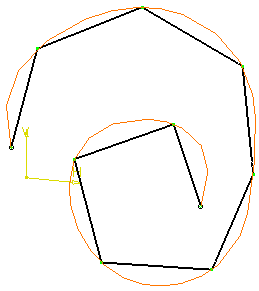
Length + Increment
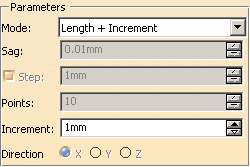
Increment:
Represents the length increment on the curve.
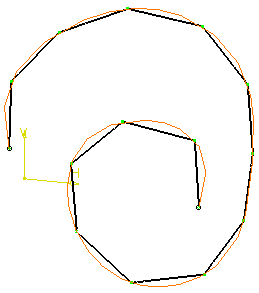
Example: Increment = 10 mm
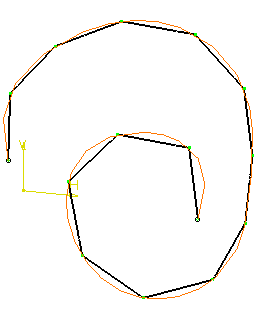
Parameter + Positions
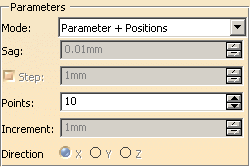
Points:
Is the number of positions N. The parameter of the curve is divided by
(N-1), providing a constant curve-parameter increment.
Example: Points = 15
Direction + Increment
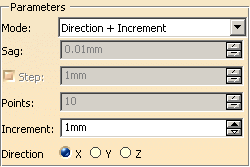
You must specify a main direction (x, y or z) in order to define a
reference plane.
The origin of the reference plane is (0, 0, 0).
Increment:
This is the distance between two consecutive planes. Points are the result
of the intersection of the planes with the curve.
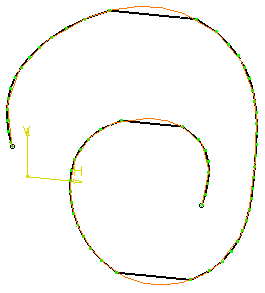
Example: Direction Y, Increment=1 mm
![]()