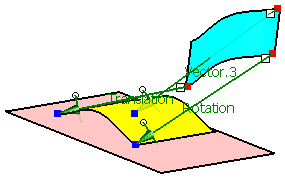
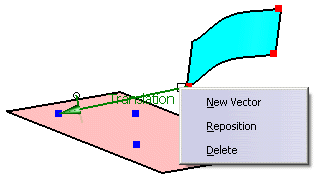
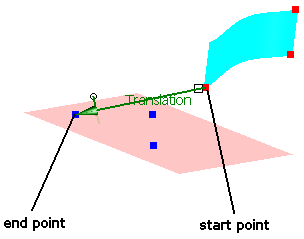
Only operations activated in the field Options are executed.
-
Click the Adjust icon:
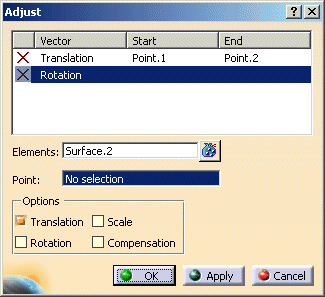
The Adjust dialog box is displayed.

-
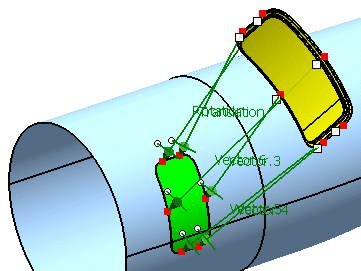
Select the door geometry to be adjusted (76 surfaces).
-
Terminate selection with F8.
In the dialog box 'Adjust', the field Point becomes active.
-
Expand the geometrical sets for 'Adjust Points' and Aperture Points.
These are the points to be used for transformation.

-
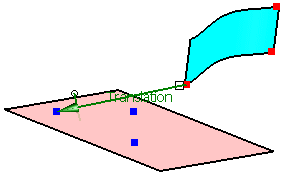
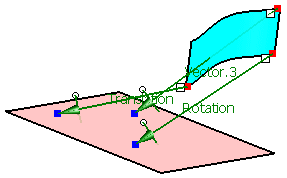
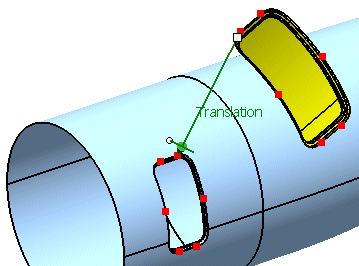
First select 'P1' from the geometrical set 'Adjust Points'
-
Next select 'p1' from the geometrical set 'Aperture Points'.

-
Activate the option 'Translation'.
-
Click Apply.
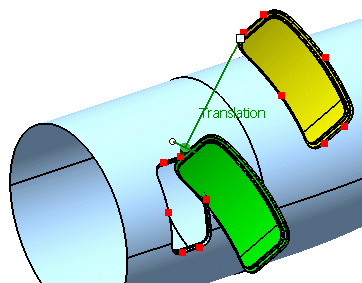
-
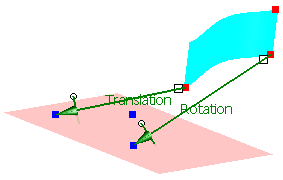
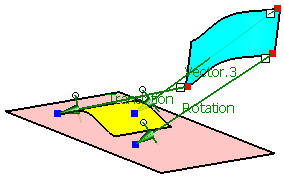
First select 'P2' from the geometrical set 'Adjust Points'
-
Next select 'p2' from the geometrical set 'Aperture Points'.
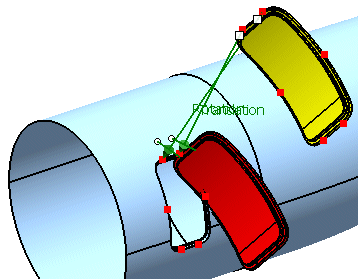
-
Activate the option 'Translation'.
-
Click Apply.
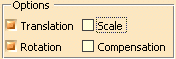
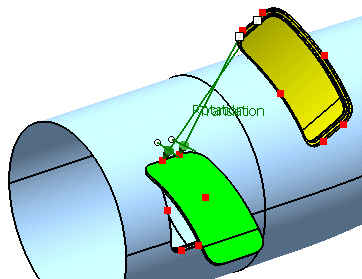
-
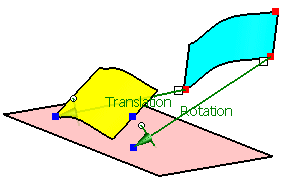
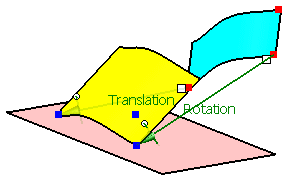
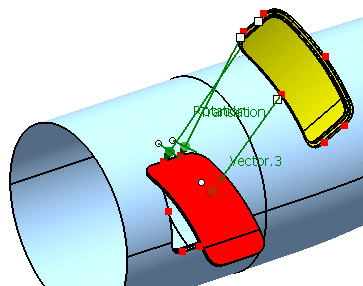
First select 'P3' from the geometrical set 'Adjust Points'
-
Next select 'p3' from the geometrical set 'Aperture Points'.
-
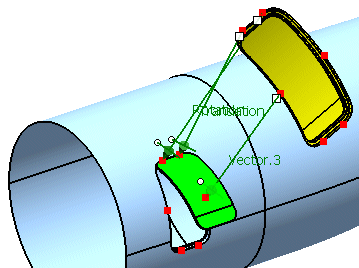
Activate the option 'Scale'.
-
Click Apply.
-
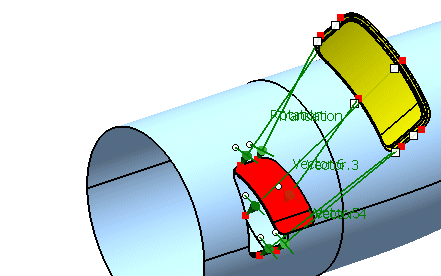
Activate the option 'Compensation'.
-
Click Apply.