About Expert Checks
The Knowledge Expert product allows you to create and manipulate
relation-type features. These particular features are organized into a
hierarchy. The rule base object is at the top of this hierarchy, the
expert rules and expert checks are the terminal objects. In
between you can find the rule sets which gather rules and checks
(see the graphic below).
 |
Creating an Expert Check:
Select the Expert Check icon to create an expert check, write its body,
test its syntax and add it to your rule base. |
 |
Generating a Check Report:
Select the Check Report icon to generate a report. Clicking this icon is
of interest when you have solved a rule base with a certain number of
checks applying to multiple features. The report gives you information on
valid and invalid checks as well as extra information depending on the
Rule Base Settings. |
- An Expert check is a relation which only checks that a condition is
true for the objects of one or more given types. They do not modify the
document they are applied to.
|
An expert check is made up of two parts:
-
The definition of the feature types the check applies to:
H:Hole
-
The check body:
H.Activity == true
The check above tests the activity of the features of Hole type
belonging to your document. An expert check is valid (the condition specified
is fulfilled for all the objects) or invalid (the condition is not fulfilled
for all the objects).
The list of objects and attributes to be used in expert rules and checks is
displayed in the object browser.
 |
Be careful when using multiple types in the (for
all)
 field.
field.
If there is no object of one type declared in the “For All” field in
the document (for example no Shell in the
document), the rule will not be executed even if there are object
sof other types declared in the “For All” field in the document (for
example one object Hole in the document). |
The icons in the specification tree turn to green(
 )
or red(
)
or red(
 )
depending on whether the checks are valid or invalid. A check which is
partially valid is red. When a check is invalid, you can find out what features
are valid or invalid by generating and editing a report. If need be, you can
also specify a correction method.
)
depending on whether the checks are valid or invalid. A check which is
partially valid is red. When a check is invalid, you can find out what features
are valid or invalid by generating and editing a report. If need be, you can
also specify a correction method.
Summary of Tasks
Here is the Knowledge Expert feature
hierarchy.
 Rule Base
Rule Base |
|
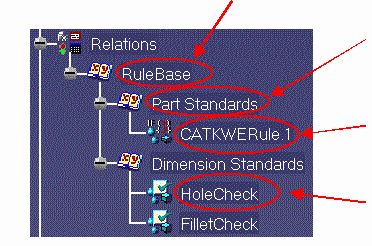 |
 Rule Set
Rule Set |
 Expert Rule
Expert Rule |
 Expert Check
Expert Check |
Creating an Expert Check
About the Check Editor
Performing an Expert Check Using the KWE Advanced Language
Editing an Expert Check
Editing the Check Name
Activating and Deactivating an Expert Check
Accessing the Expert Check in the Check Body
Highlighting Invalid Features
Generating a Check Report
Using the Check Analysis Tool
Performing a Global Analysis of Checks
Customizing Check Reports
