-
Click Chamfer
 .
.
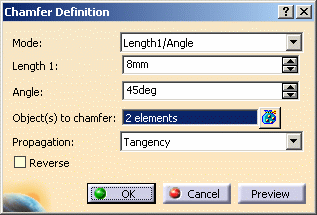
The Chamfer Definition dialog box appears. The default parameters to be defined are Length1 and Angle. You can change this creation mode and set Length1 and Length2. -
Select the edges to be chamfered.
Chamfers can be created by selecting a face: the application chamfers its edges.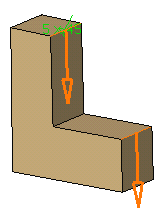
-
Keep the default mode: enter a length value and an angle value.
-
Optionally, click Preview to see the chamfers to be created.
The application previews the chamfers with the given values.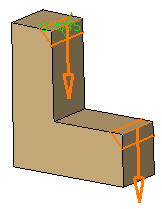
Propagation
Two propagation modes are available:
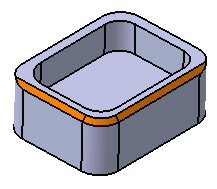
- Minimal: edges tangent to selected edges can be taken into account to some extent. The application continues chamfering beyond the selected edge whenever it cannot do otherwise. In our example below, the chamfer is computed on the selected edge and on a portion of tangent edges:
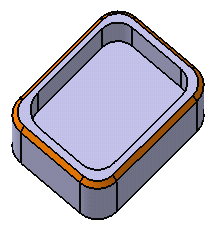
- Tangency: the application chamfers the entire selected edge as well as its tangent edges. It continues chamfering beyond the selected edge until it encounters an edge that is non-continuous in tangency as shown in our example:
-
Click OK.
The specification tree indicates this creation. These are your chamfers: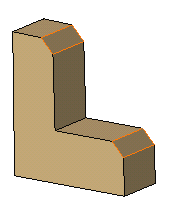
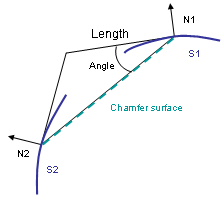
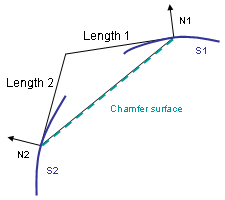
How Chamfers are Computed
The system uses the intersection of the two perpendiculars of the normal lines on supports to define the distances and angle values. The edge between the two surfaces is not used by the chamfer computation.
Chamfer Length-Length
Chamfer Length-Angle