Creating Groups
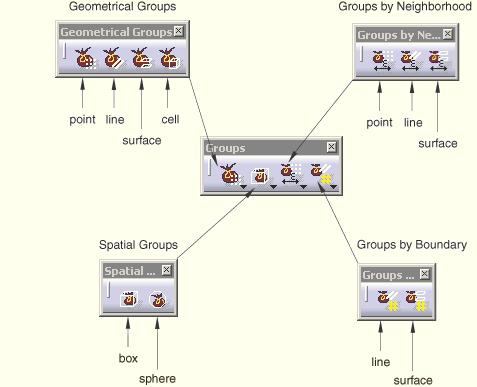
All of the CATIA V5 groups are supported by Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis. You create groups by selecting geometry (cells, faces, edges, or vertices) from your model. Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis use your selection to create a geometry group (such as a group of faces) or a group under a mesh part (such as a group of nodes). Figure 8–1 shows the tools that are available for creating groups.
Groups in Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis indicates when you can use a group as a support for an Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis feature, such as a boundary condition, a load, or a contact definition.The Geometrical Groups tools allow you to select individual vertices, edges, faces, or cells. For example, if you are creating a pressure load, you can select a group that contains surfaces, and the pressure is applied to those surfaces. Similarly, you can apply a point load to a group that contains points, and you can apply an initial temperature to a group that contains bodies.
The Spatial Groups tools allow you to select all of the entities inside a box or sphere. You can move the box or sphere around your model, and you can also resize it. Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis do not distinguish between box and sphere groups.
The Groups by Neighborhood tools allow you to select all of the vertices, edges, or faces within a specified distance of a selected vertex, edge, or face.
The Groups by Boundary tools allow you to select lines and edges that connect to form a closed polygon, and Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis select all the nodes and elements inside the polygon. You can also select connected surfaces and faces that form a closed shape, and Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis select all the nodes and elements inside the shape.
Groups are useful when you have a complex model that requires extensive view manipulations to select the desired entities. Groups are also useful when you are repeatedly selecting the same entities to support different operations. To simplify your selection, you can name a group and select the group from the specification tree, as shown in Figure 8–2.
You create a group under the mesh part by right-clicking on the mesh part in the specification tree and selecting Create Group from the menu that appears. Figure 8–3 shows the tools that are available for creating mesh groups.
In some cases, you can select only groups that are under a mesh part; for example, when you are selecting the component of a general analysis connection or a rigid coupling. When you update a mesh part, Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis do not update the groups under the mesh part. You must update each group by right-clicking the mesh groups in the specification tree and selecting Update Group from the menu that appears. You must select a group under a mesh part when you are creating the following Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis entities (or selecting their handler points):-
Rigid body constraints
-
Rigid and smooth couplings
-
Analytical rigid surfaces
-
Springs
Groups by neighborhood are useful for creating groups under mesh parts where suitable geometry, from which you would otherwise create a geometrical group, does not exist. For example, you cannot create a face group from a mesh part that was extruded from a surface because there is no geometry extending beyond the original surface. However, you can select faces from the mesh part and create a face group under a mesh part.
Groups that you create with the Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis workbenches become Abaqus node sets and/or element sets. You can right-click on a geometry group or a group under a mesh part in the specification tree and select Analyze Group to determine the number of nodes, elements, element faces, and element edges in the group. The name of the group is included in the Abaqus set name. All groups in the specification tree are written to the Abaqus input file, regardless of whether they are used by Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis.
Groups in Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis shows how Nonlinear Structural Analysis and Thermal Analysis use CATIA V5 groups to create node or element sets that can be analyzed by Abaqus.