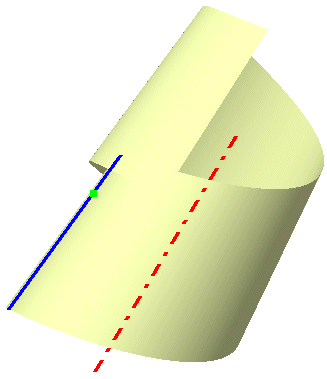
The command Helix creates a helical surface, by gradually displacing the guide along the rotation axis at the same time as it rotates about this axis. The resulting surface is referred to as a helicoid.
Open the Helix.CATPart document.
-
Click the Helix icon
 .
.
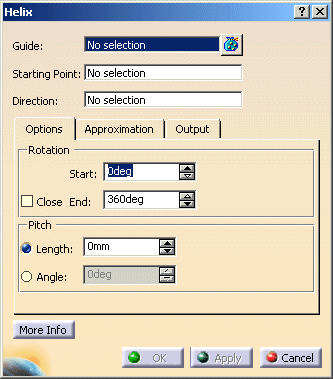
The Helix Surface Definition dialog box appears.
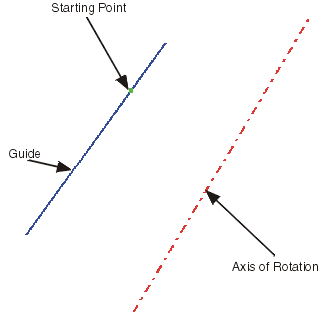
The model contains 3 geometry elements.
-
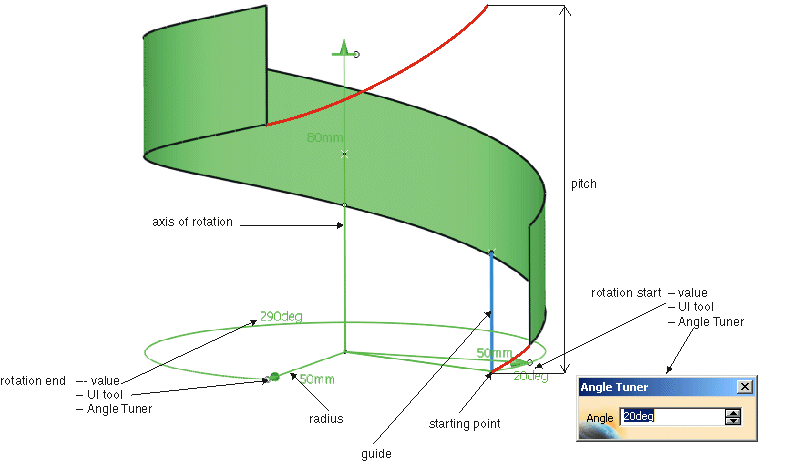
Select the Guide, the Starting Point and the Direction (axis of rotation).
-
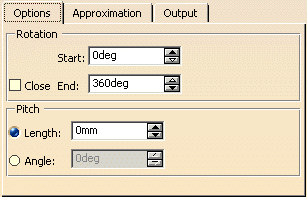
Set start angle to 0° and end angle to 90°.
-
Set length to 0 mm.
-
Click Apply.
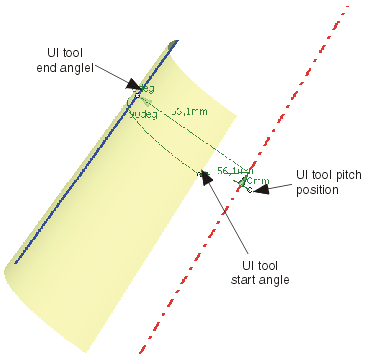
Start and end angle as well as the pitch can be modified dynamically using the manipulators.
-
Select the manipulators for start and end angle and modify the angles.

-
Select the manipulator for pitch position and draw it along the axis of rotation.
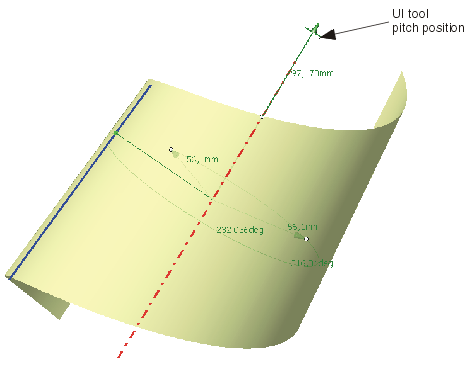
By default, the input range for start and end angle is from 0° to 360°. This range can be modfied:
-
Activate the context menu by clicking the right mouse button on the text field End and the option Range > Edit....
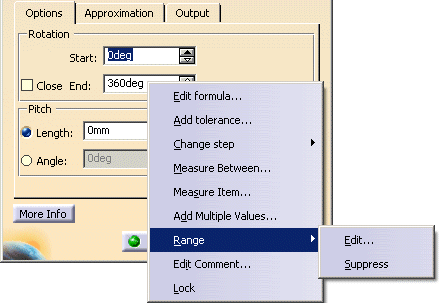
-
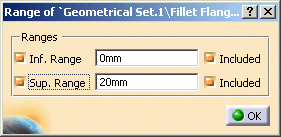
Set in the dialog box 'Range' the Sup. Range to 720° and close the window with OK.
-
Set in the dialog box 'Helix' the start angle to 0° and the end angle to 450 °.
-
Click OK to create the helical surface.