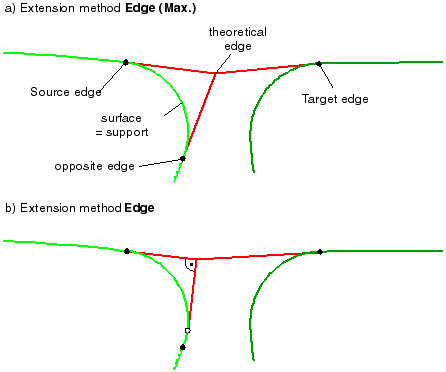
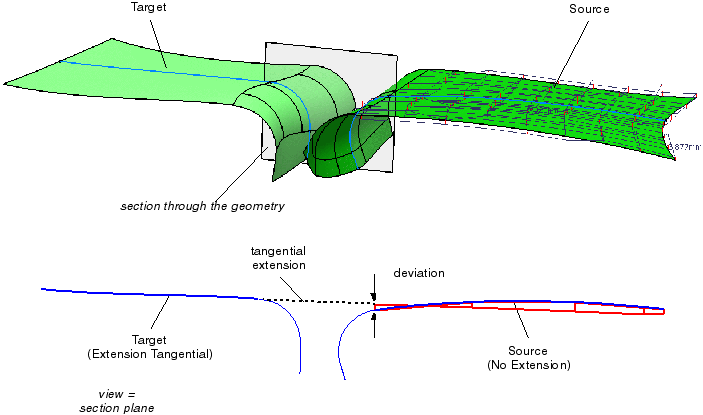
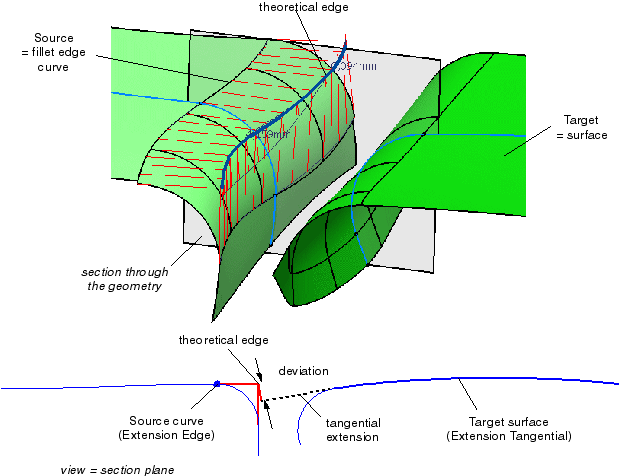
| |
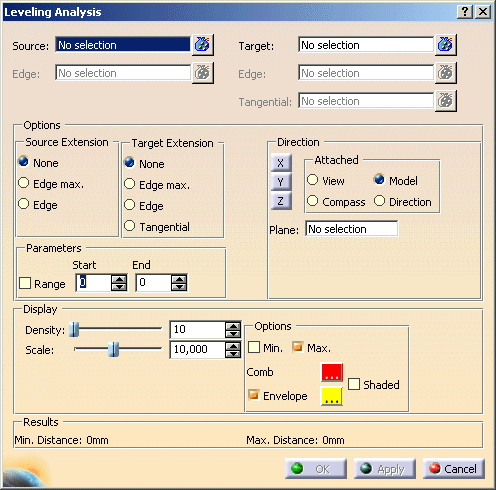
- Parameters:
- Range: Start/End: Specification of a value range for an optimum deviation. Only those deviation values
that are lying outside of the defined range are taken into consideration. The numerical display indicates the minimum
and/or maximum deviation value that is independent from the defined range.
- System: Here you can define, which component of the minimum and/or maximum deviation shall be computed and
displayed numerically, and which coordinate system shall be used for this.
| System |
Direction: X, Y, Z |
Direction: 3D |
Model
(model coordinate system) |
specified coordinate system is valid for calculating the X, Y, or Z/Depth coordinate of the deviation |
3D deviation is calculated in space (no projection) |
Plane
(coordinate system of the selected plane) |
3D deviation is projected into the specified plane |
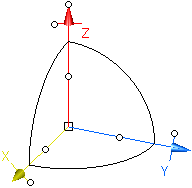
User-Defined
(user-defined coordinate system which can be additionally modified by the 3D manipulator in the graphics area) |
 |
View
(view plane) |
Compass
(compass plane) |
 |
Note: The 3D manipulator is independent from the view and compass position, i. e. in case of view and
compass manipulations the manipulator will not be moved accordingly. |
- Display
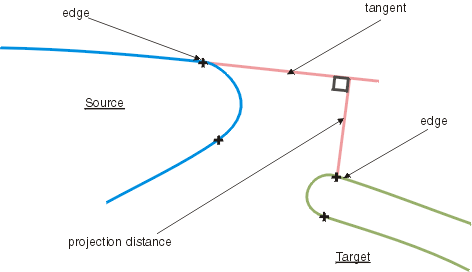
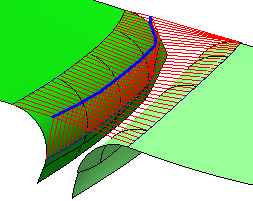
- Density: The number of points specified here are regularly distributed on the Source (on patches and faces
in U and V direction) and projected onto the Target.
- Scale: Scaling factor for the display of the deviation values.
|