This task explains how to process geometry for a more efficient data management.
To address the data management process in a more efficient manner, ISD commands must be designed in a way that they can handle data coming from everywhere.
Within the Class A process, the more traditional approach for users is to obtain geometry output of a maximum order 7 and by having less segments and with a minimum Deviation from the original Input geometry. As this is not always possible users prefer to have better control over the output.
-
Click the Curve Conversion icon
 .
.
The Curve Conversion dialog box opens.
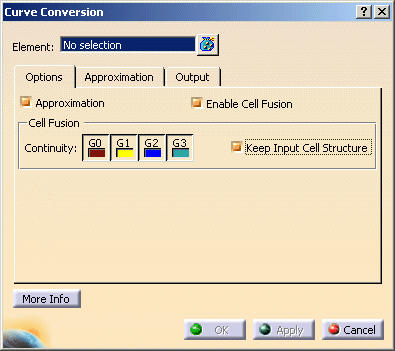
- Element: Specifies the curves to be processed.
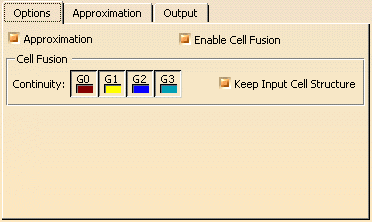
- Approximation: The approximation options can be deactivated. This way, you can e. g. create curves from surface edges without approximation.
- Enable Cell Fusion:
- OFF: Each cell of a Domain will be approximated separately.
The Cell Fusion options are not available. - ON: All adjacent cells of a domain whose transition quality among each other corresponds at least the value specified
in Continuity, are approximated as one entity (segmentation of the domain
in continuity ranges).
The Segmentation will be applied to each continuity range.
The transition parameters will be used as preferential parameters for further processing with the settings on the Approximation tab.
- OFF: Each cell of a Domain will be approximated separately.
- Cell Fusion: The Cell Fusion options are only available if
Enable Cell Fusion is activaed.
- Continuity: The cells are only merged if at least the specified continuity is
kept.
To keep the number of segments as low as possible, when using G0 continuity, the tolerance will not be considered when approximating, independent from the approximation parameters set. - Keep Input Cell Structure: The geometry resulting from the approximation will be re-broken at the transitions after the approximation operation.
- Continuity: The cells are only merged if at least the specified continuity is
kept.
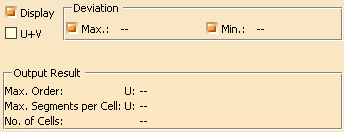
- Display: Depending on the options selected, values are displayed in the graphics area.
- Deviation:
- Max., Min.: Shows the minimum and/or maximum deviation between the input element and the resulting output
geometry, e. g. between a guide curve (input) and the resulting surface boundary (output).
Depending on the result you can change parameters and options to improve the resulting geometry.
- Max., Min.: Shows the minimum and/or maximum deviation between the input element and the resulting output
geometry, e. g. between a guide curve (input) and the resulting surface boundary (output).
- U+V: Display of the UV vectors of curves and surfaces.
- Output Result: See Output Result