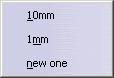|
This task explains how to create a flange from a reference curve. |
 |
Flange surfaces are composed successively from ruled surfaces.
A flange surface can start from the guide curve or from a target surface. Length and Angle define extent and direction of the
flange surface. The basic flange direction is the direction with a flange angle of 0°.

The order of the flange surface in direction of the guide curve
will be adopted from the guide curve. The order perpendicular to the guide curve will always be 2. The guide curve
- can exist for itself, without a surface, 3D-Curve
- can be connected with a surface, 2D-Curve
- can be the edge of a surface
|
 |
Open the Flange.CATPart document. |
 |
-
Click the Flange icon  . .
The Flange dialog box opens.
|

|
| |
-
Select the edge of the surface where you want to create the flange.
|
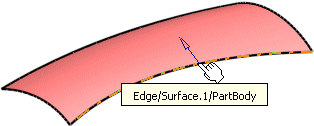
|
| |
-
Select as Alignment Patch Normal and Surface.1 as reference Surface.
-
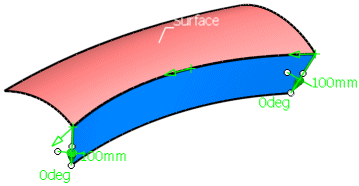
Enter a Length of 100mm and click Apply. The flange surface and two vectors
are displayed.
|
 |
| |
-
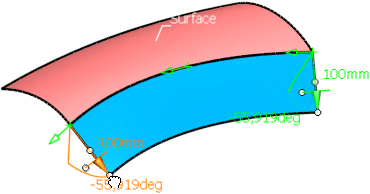
Change the angle by drawing the first handle at the manipulator tip.
|
 |
| |
-
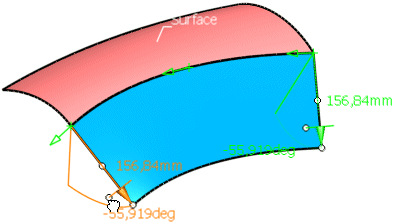
Change the length by drawing the second handle at the base of the manipulator tip.
|
 |
| |
-
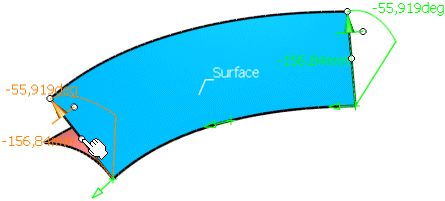
Invert the flange direction by clicking onto the middle handle of the manipulator.
|
 |
| |
-
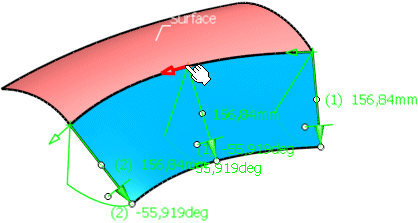
Undo the inversion. Click into the middle of the guide and move the cursor to insert another manipulator.
|
 |
| |
-
Specify an individual length and angle by modifying the middle manipulator.
|
 |
| |
-
Click OK to create the final flange surface.
|
 |
 |
You can define the following options:
- Alignment: The basic flange direction runs in normal direction of the base surface, if surface edges have been
selected as guide curve, or in normal direction of the target surface, if the guide curve is a curve segment or curve.
- Patch Normal: The normals of the surface edge selected as guide define the flange
direction.

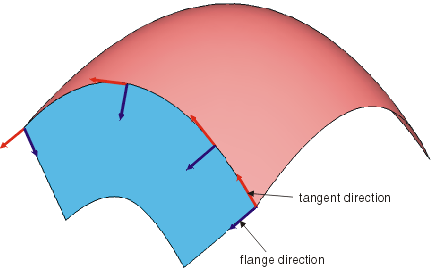
- Guide + Prio. Tangent: The flange direction is generated from a moving frame type that is tangent to the
guide curve direction and is orientated depending upon the direction chosen.
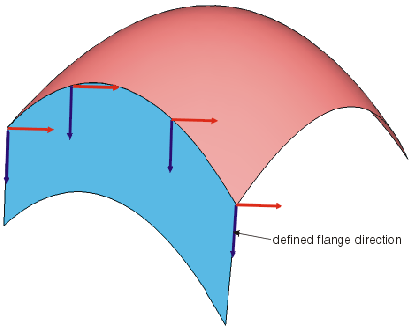
- Guide + Prio. Direction: The flange direction is taken from a direction defined from the Direction field.
- Moving Frame: The flange direction can be defined by a Moving Frame (see 'Moving
Frame' tab).

|
| |
- Guide: Specifies the guide curve.
- Surface: If a curve is selected, the flange is created in normal direction of an individual surface.
|
| |
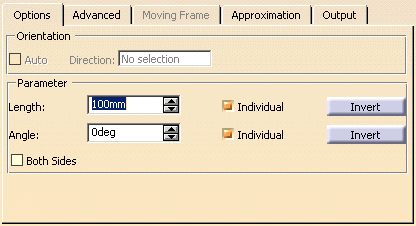
Options tab |
 |
| |
- Orientation:
- Auto: This option is only available for the Guide + Prio. Tangent and Guide + Prio. Direction
options.
You can choose to allow the definition for the orientation of the Flange to be calculated automatically via a local Z
axis.
- Direction: The flange direction can be specified manually.
- Length: Defines the main length of the Flange.
- Individual: You can specify an individual length between start and end point.
- Invert: Inverts the flange direction.
- Angle: Defines the angle of the Flange with respect to the selected Alignment options.
- Individual: You can specify an individual angle between start and end point.
- Invert: Inverts the flange angle.
- Both Sides: Creates a Flange surface in both directions of the Flange Alignment.
|
| |
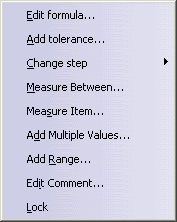
For the options Length and Angle the following contextual menu is available:
- Edit formula...: Enables you to edit a formula, see
About the Formula Editor.
- Add tolerance...: Enables you to edit tolerances.
- Change step: The values for Length and Angle can be modified by 1 mm or the specified step size. The step size
can be modified via new one.
- Measure between... : see Measuring
Distances between Geometrical Entities.
- Measure Item...: see Measuring Properties.
- Add Multiple Values...: Enables you to add multiple values for the object.
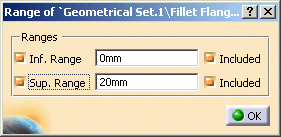
- Add Range...: For Length and Angle, you can specify values within a range.
With this option a dialog box is activated, in which you can modify the values for the inferior and superior range. With the
option Included, the inferior and superior limit values are included.
- Edit Comment... Enables you to add a comment.
- Lock: Enables you to lock a parameter.
|
 |
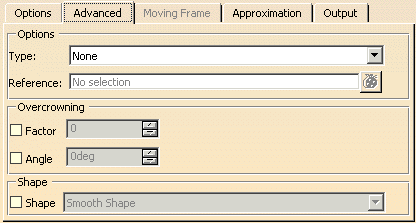
Advanced tab (in ISD only) |
 |
| |
- Type
- None: Nothing is defined.
- Target: Starts from Target when switched on the Target option moves the result to the Target surface(s) using
the guide curve and Angle as input.
The target surface has to be selected via Reference.
- Connect: Defines the length of the Flange surface between the Guide and the Target surface.
- Overcrowning: The created flange surface can be overcrowned either by specifying a crowning factor or a draft
angle.
When Overcrowning option is switched on, Both Sides option is disabled.
- Factor: The flange surface is overcrowned with the specified factor. The crowning factor defines the chordial
depth with respect to the linear length of the fange which is defined between the guide curve and the end of the flange
The crown value is applied at the mid point along the flange length.l

- Draft Angle: Defines the minimum draft angle allowed at the end position of the flange depth with respect
to the alignment direction chosen.
The flange shape passes through 3 points to create a smooth evolution:
- Draft direction
- Crown factor position
- Guide curve

- Shape: Type of Transition: Specifies the shape of the surface, i. e. the transition type between the individual
selected Flange sections (Default: Smooth Shape):
|
Linear Shape
|
Local Shape
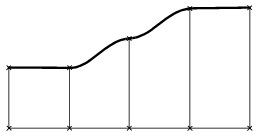
|
Smooth Shape
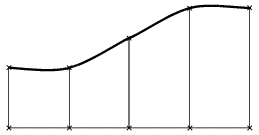
|
Global Shape
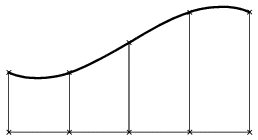
|
|
 |
See Moving Frame tab (in ISD only) |
| |
See Approximation tab |
| |
See Output tab |
| |
Click onto the 'More Info' button to display deviations and output results. |
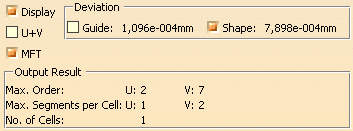 |
| |
- Display: Depending on the options selected, values are displayed in the graphics area.
- Deviation:
- Guide: Displays the deviation of the approximated guide.
- Shape: Displays the deviation from the flange.
- U+V: Display of the UV vectors of curves and surfaces.
- MFT: Display of the local coordinate system for the moving frame type.
- Output Result: See Output Result
|
| |
Manipulators and context menus
|
| |
The created flange surface can be modified as follows using the manipulators:
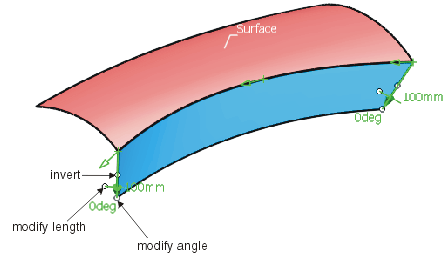
Moving the drag manipulator on the guide, you can add additional manipulators allowing to specify individual lengths and angles:
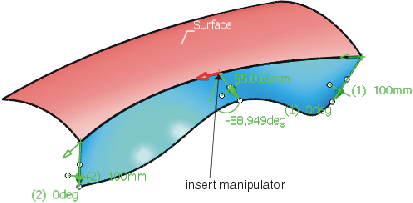
The flange surface can be restricted to a partial region:

|
 |
Note: Pressing the control key allows simultaneous manipulations of length and angle. In this case,
however, individual values will be equated. |
| |
At the manipulator handles for Length and Angle, you can activate with the right mouse button context menus with the following
options:
- Edit Angle (for angle modification only): The dialog box 'Angle Tuner' to specify a new angle value is activated.
- Keep Point (for angle modification only): A point is created at the current position of the manipulator.
- Spread all (for angle and length modification only): The current value is assigned to all other manipulators.
- Edit Position (for additionally inserted manipulators only): Changes the manipulator position.
- Delete (for additionally inserted manipulators only): Deletes the manipulator.
At the drag manipulators, you can activate with the right mouse button a context menu with the following options:
- Edit Position: Changes the manipulator position.
- Freeze:
- Keep this point:
|
|

|

 .
.